

The process for treating these materials includes the following: (a) acid leaching, (b) purification of the leach liquors using sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide, (c) precipitation of yttrium using oxalic acid, and (d) calcinations of oxalates for production of yttrium oxides. Abstract: In this paper, yttrium recovery from fluorescent powder of lamps and cathode ray tubes (CRTs) is described. • Economic simulation for the processes to recover yttrium from WEEE. • Recovery of yttrium from fluorescent powders. • Fluorescent powder of cathode ray rubes. Highlights: • Fluorescent powder of lamps.
Recovery of yttrium from cathode ray tubes and lamps’ fluorescent powders: experimental results and economic simulation A first version of a mock-up is presented, and experimental results are presented and discussed. In the next part, the author addresses some theoretical aspects of corrections to be made for spot deflection, spot focussing, and spot brightness. The author describes a cathode ray tube, presents different methods to obtain a colour image (mask tube, electron penetration tube, and intensity change tube), discusses the choice of a cathode ray tube type, and describes its use in a display console. The objective of this research thesis is to study the possibility to obtain a colour image which can be used in cathode ray tube display console. Use of an electron penetration cathode ray tube in a colour display console The experimental results reviewed here include A-site and B-site segregations, lattice expansion, oxidation-state changes during cell operations and liquid-phase infiltration and coarsening of cathode to electrolyte backbone The epitaxial thin film model cathodes for XR, TXRF, and HRD measurements are made by pulse laser deposition and porous film cathodes for USAX measurements are made by screen printing technique.
The X- ray techniques used include X- ray reflectivity (XR), total-reflection X- ray fluorescence (TXRF), high-resolution diffraction (HRD), ultra-small angle X- ray scattering (USAXS). Abstract: Synchrotron-based X- ray techniques have been used to study in situ the structural and chemical changes of film cathodes during half-cell operations. •Liquid-phase infiltration and coarsening processes of cathode materials into porous YSZ electrolyte backbone were monitored by USAXS. •The surface and subsurface of the LSM and LSCF films have different oxidation-states due to vacancy concentration changes. •Chemical lattice expansions show that oxygen- cathode interface is the primary source of rate-limiting processes.
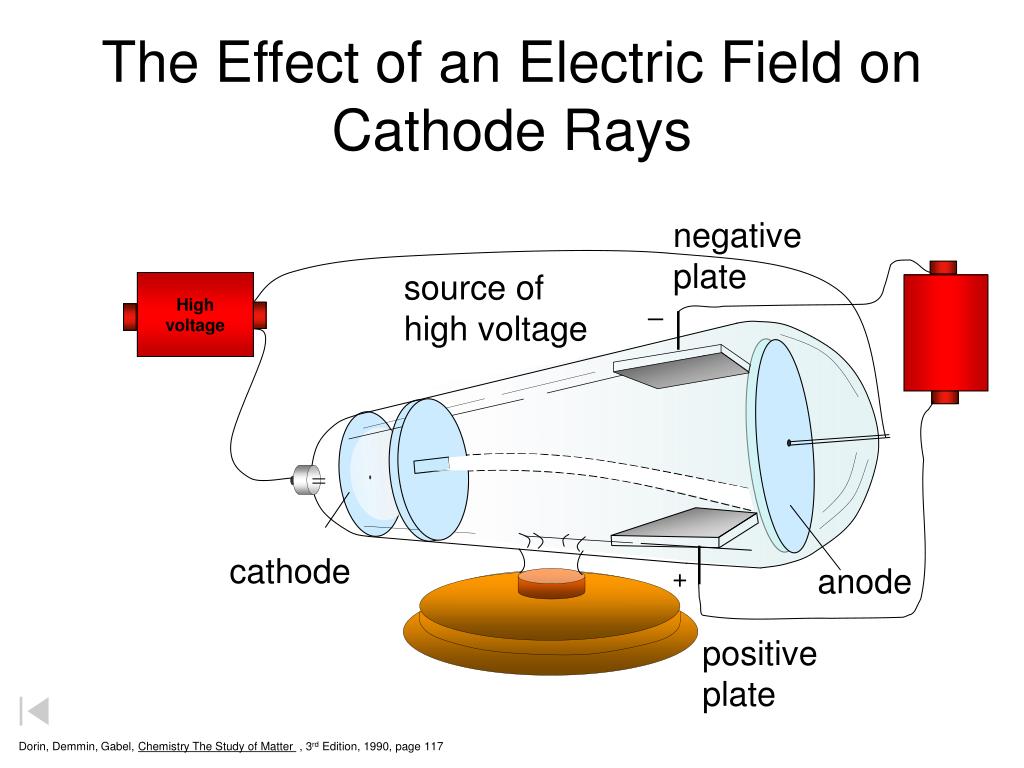
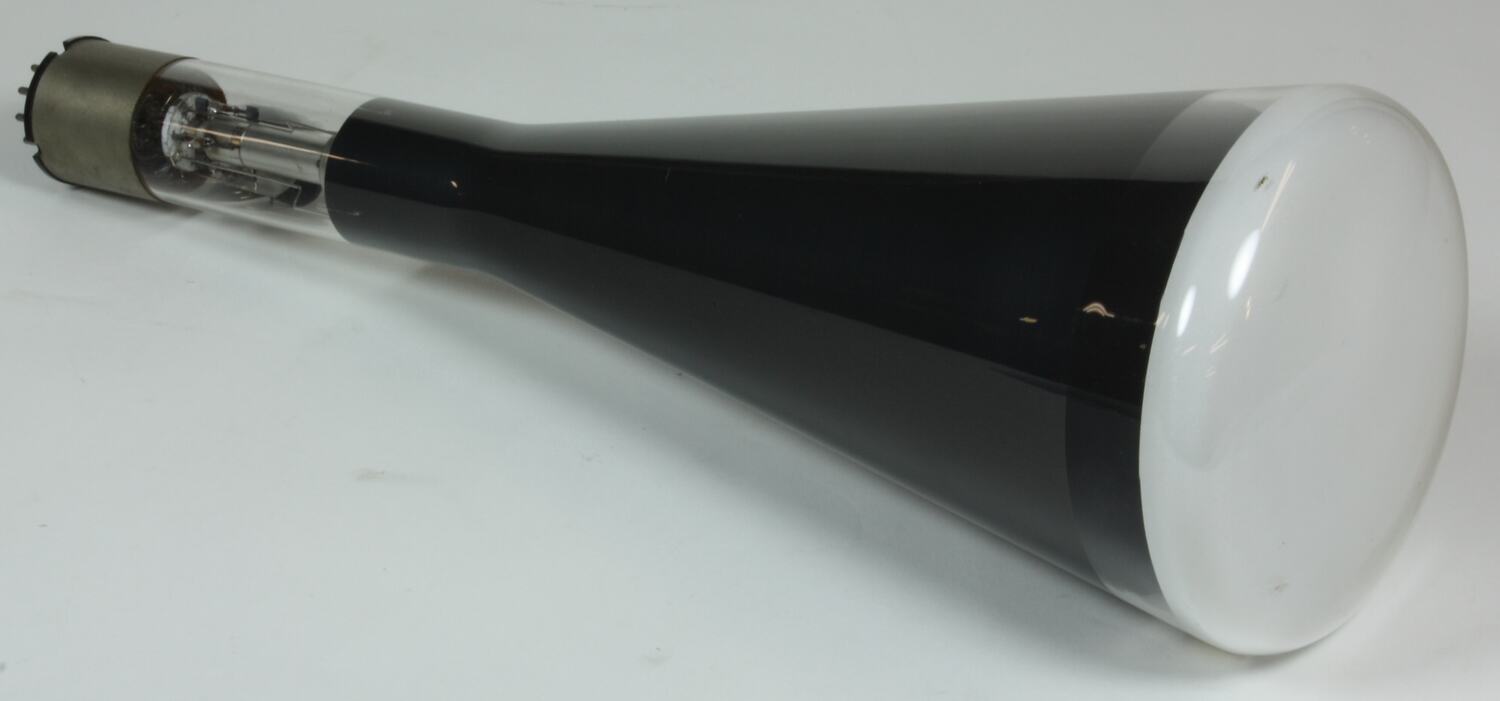
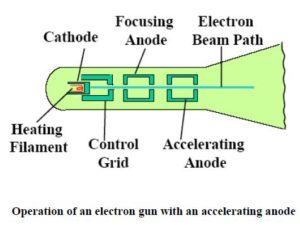
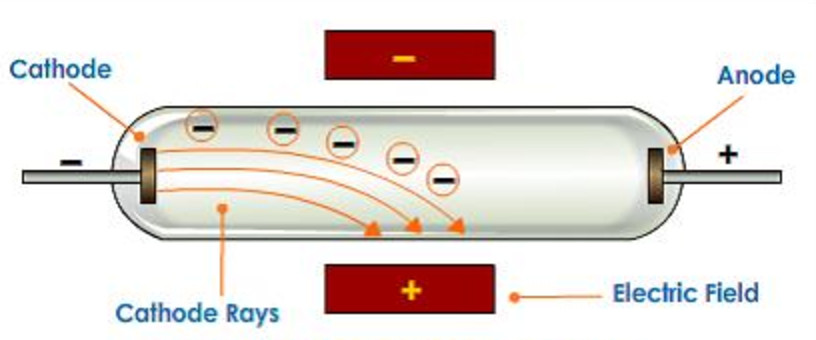
•A-site and B-site cations actively segregate or desegregate on the changes of temperature, pO 2, and electrochemical potential. Highlights: •Synchrotron X- rays are used to study in operando the structural and chemical changes of LSM and LSCF film cathodes during half-cell operations. International Nuclear Information System (INIS)įuoss, Paul Chang, Kee-Chul You, Hoydoo These particles were named electrons.In situ X- ray studies of film cathodes for solid oxide fuel cells This shows that cathode rays are negatively charged particles. This shows that these rays consist of material particles having both mass and velocity.ģ. Cathode rays produce green fluorescence upon striking glass or certain other materials.Ĥ. When cathode rays are allowed to strike on a piece of metal foil, it becomes hot which shows that these rays produce heating effect.ĥ. These rays ionise the gas through which they pass.Ħ. These rays produce X-rays when they strike against hard metals such as tungsten.ħ. When an electric or magnetic field is applied on the cathode rays, they are deflected from their straight path towards the positive plate of the electric field. These rays are called cathode rays.ġ. Cathode rays travel in a straight line.Ģ. Cathode rays rotate the light paddle wheel when placed in their path. Production of cathode rays: When a current of high voltage (10000 volts) is passed through a gas or air kept at a very low pressure (0.01 -0.03 mm) contained in a discharge tube, blue rays are seen emerging from the cathode which produce a fluorescence on the walls of the discharge tube.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
